Blog Layout
Diabetes - Sugar Control
DJAB • September 28, 2020
SUGAR - The Fuel ⛽️ for Diabetes.
As hunter-gatherers, we ate the equivalent of only 20 teaspoons of sugar a year. Today, we eat over 150 pounds per year per person, or half a pound a day. The average school kid eats 34 teaspoons of sugar a day.
Food manufacturers realize you know the usual suspects, so they’ve become savvier. Many supermarkets and health food stores now carry many sneaky sources of sugar, disguised in unrecognizable ingredients and so-called healthy foods that contain as much if not more sugar than their regular versions.
The Diabetes Epidemic
The number of people diagnosed with diabetes world-wide in the last 20 years has increased explosively and can now be considered as a diabetes "epidemic". Long considered a disease of minor significance to world health, it is now viewed as a major threat to human health in the 21st century. The global incidence of the disease is set to rise from the current estimation of 150 million, to 220 million by 2010, and to 300 million by 2025. In developed countries the number of people with Diabetes will increase by 42% by 2025, while the increase in lesser developed countries is expected to be 170%. Diabetes used to occur mainly in middle age people, but today it is becoming very common in children.
Diabetes occurs when refined sugars are eaten too often and too fast, causing large swings in blood sugar levels. Although you don’t necessarily "feel" poor glucose levels, Diabetes reduces your quality of life because it causes so many other conditions that make you feel bad. Diabetes can lead to heart attacks, kidney and eye problems, and possible amputation of feet and legs over time.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a serious complex condition which can affect the entire body. Diabetes requires daily self care and if complications develop, diabetes can have a significant impact on quality of life and can reduce life expectancy. While there is currently no cure for diabetes, you can live an enjoyable life by learning about the condition and effectively managing it.
There are different types of diabetes; all types are complex and serious. The three main types of diabetes are type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes.
How does diabetes affect the body?
When someone has diabetes, their body can’t maintain healthy levels of glucose in the blood. Glucose is a form of sugar which is the main source of energy for our bodies. Unhealthy levels of glucose in the blood can lead to long term and short term health complications.
For our bodies to work properly we need to convert glucose (sugar) from food into energy. A hormone called insulin is essential for the conversion of glucose into energy. In people with diabetes, insulin is no longer produced or not produced in sufficient amounts by the body. When people with diabetes eat glucose, which is in foods such as breads, cereals, fruit and starchy vegetables, legumes, milk, yoghurt and sweets, it can’t be converted into energy.
Instead of being turned into energy the glucose stays in the blood resulting in high blood glucose levels. After eating, the glucose is carried around your body in your blood. Your blood glucose level is called glycaemia. Blood glucose levels can be monitored and managed through self care and treatment.
Three things you need to know about diabetes:
- It is not one condition- there are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes
- All types of diabetes are complex and require daily care and management
- Diabetes does not discriminate, anyone can develop diabetes
Diabetes can be managed well but the potential complications are the same for type 1 and type 2 diabetes including heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, limb amputation, depression, anxiety and blindness.
We know diabetes:
- Is the leading cause of blindness in working age adults
- Is a leading cause of kidney failure and dialysis
- Increases the risk of heart attacks and stroke by up to four times
- Is a major cause of limb amputations
- Affects mental health as well as physical health. Depression, anxiety and distress occur in more than 30% of all people with diabetes
Early diagnosis, optimal treatment and effective ongoing support and management reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Why is diabetes increasing?
All types of diabetes are increasing in prevalence:
- Type 1 diabetes accounts for 10% of all diabetes and is increasing
- Type 2 diabetes accounts for 85% of all diabetes and is increasing
- Gestational diabetes in pregnancy is increasing
Type 2 diabetes is increasing at the fastest rate. There are large numbers of people with silent, undiagnosed type 2 diabetes which may be damaging their bodies. An estimated 2 million Australians are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and are already showing early signs of the condition.
Type 2 diabetes is one of the major consequences of the obesity epidemic. The combination of massive changes to diet and the food supply, combined with massive changes to physical activity with more sedentary work and less activity, means most populations are seeing more type 2 diabetes.
Genes also play a part with higher risk of type 2 diabetes in Chinese, South Asian, Indian, Pacific Islander and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations.
Symptoms
In type 1 diabetes, symptoms are often sudden and can be life-threatening; therefore it is usually diagnosed quite quickly. In type 2 diabetes, many people have no symptoms at all, while other signs can go unnoticed being seen as part of ‘getting older’.
Therefore, by the time symptoms are noticed, complications of diabetes may already be present.
Common symptoms include:
- Being more thirsty than usual
- Passing more urine
- Feeling tired and lethargic
- Always feeling hungry
- Having cuts that heal slowly
- Itching, skin infections
- Blurred vision
- Unexplained weight loss (type 1)
- Gradually putting on weight (type 2)
- Mood swings
- Headaches
- Feeling dizzy
- Leg cramps
Note: This information is of a general nature only and should not be substituted for medical advice or used to alter medical therapy. It does not replace consultations with qualified healthcare professionals to meet your individual medical needs.
Consider......
- Emulin® is a naturally derived compound that has the unique ability to "buffer" and "quelch" the effects of glucose on the human metabolic pathway which will be instrumental in treating hyperglycemia and hopefully improve the lives of diabetics worldwide.
- Emulin® is an incredible discovery. It is a whole new way of attacking the problems of diabetes and metabolic syndrome, the precursor of diabetes. Metabolic Syndrome is a disorder of aging which is made up of five symptoms which are often seen together and predict diabetes
- Obesity – especially around the waist.
- High blood pressure.
- High cholesterol.
- High triglycerides.
- High fasting blood glucose levels.
Emulin® works by a combination approach to mitigate the damage cause by hyperglycemia from the diet by its insulinomimetic affects.
Emulin® can assist and support:
- Reduce the dietary absorption of carbohydrates in the upper G.I.
- Reduce Glucose Synthesis in the Liver.
- Accelerate Glucose Uptake from the bloodstream.
- Mobilize carbohydrates (glucose) from adipocytes.
- Increase the sensitivity of Insulin receptors in the signaling pathways – this makes insulin more efficient.
Thank you for your support in reading this article and hopefully you have found it beneficial.
"Providing Better Health Through Knowledge"

By DJAB
•
April 8, 2022
Glutathione - Collagen - L-Carnitine - Vitamin C
Four ingredients when taken alone can certainly support the body and provide added benefits. However, combined them together and you definitely will have the opportunity to not only feel, but see improvements.
Knowledge is like adding another book to your library.
“People Helping People in Health and Wellness”

By DJAB
•
January 9, 2022
Why Detoxing is Beneficial.
Detoxification — or detox — is a popular buzzword.
It typically implies following a specific diet or using special products that claim to rid your body of toxins, thereby improving health and promoting weight loss.
Fortunately, your body is well-equipped to eliminate toxins and doesn’t require special diets or expensive supplements to do so.
That said, you can enhance your body’s natural detoxification system.
Thank you for your support in reading this article and hopefully, you have found it beneficial.
"Providing Better Health Through Knowledge"

By DJAB
•
November 24, 2021
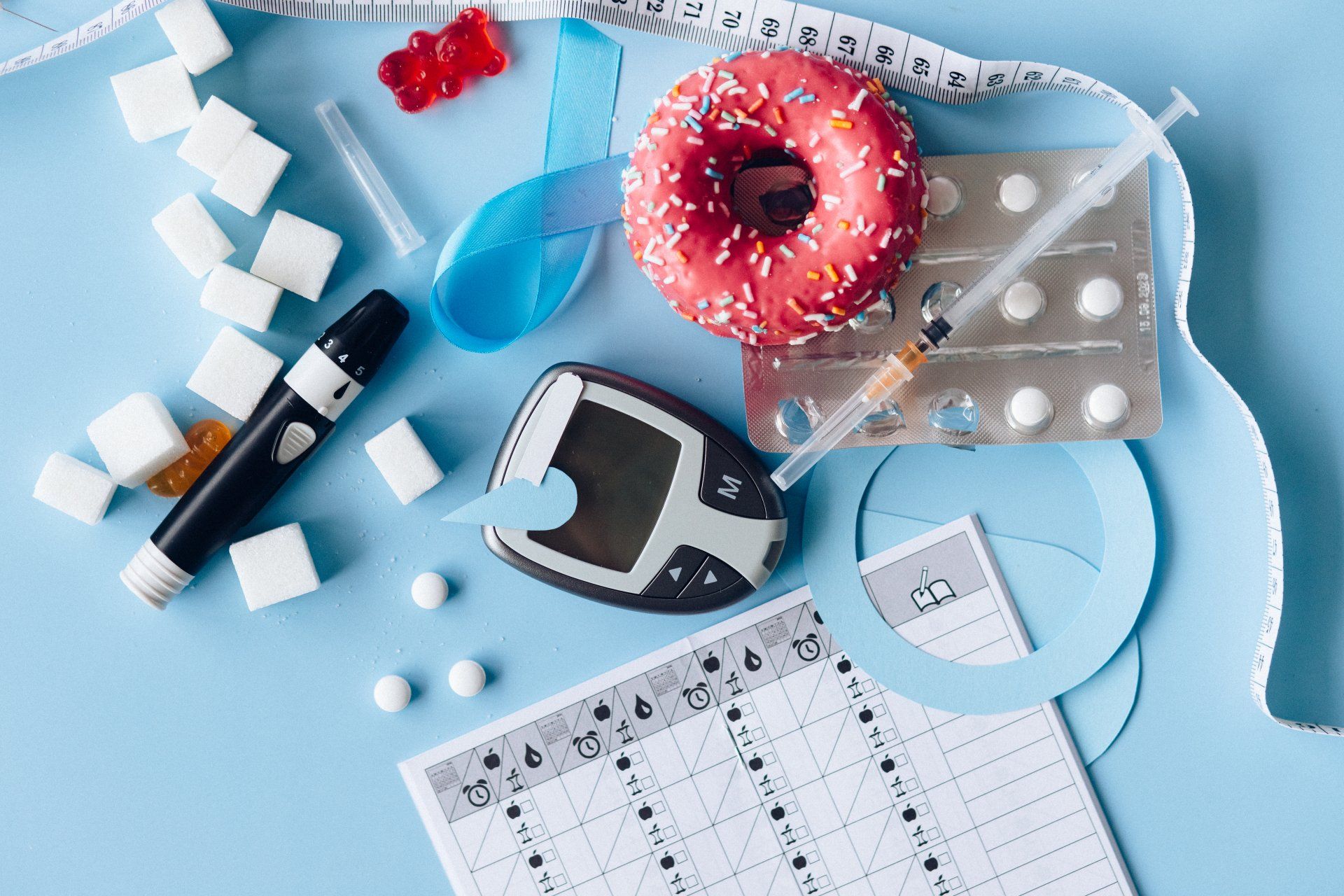
Many people rely on quick, processed foods for meals and snacks. Since these products often contain added sugar, it makes up a large proportion of their daily calorie intake.
In the US, added sugars account for up to 17% of the total calorie intake of adults and up to 14% for children.
Dietary guidelines suggest limiting calories from added sugar to less than 10% per day.
It is believed that sugar consumption is a major cause of obesity and many chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes.
Here are some reasons why eating too much sugar is bad for your health.
Thank you for your support in reading this article and hopefully, you have found it beneficial.
"Providing Better Health Through Knowledge"
Disclaimer: All content and media on this website is created and published online for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice and should not be relied on as health or personal advice.
Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. Never disregard the advice of a medical professional, or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
"Copyright 2021. Dr. Joseph Ahrens and Logo are trademarks of Dr. Joseph Ahrens LLC. All rights reserved."

